
Practical Programmable Circuits: A Guide to PLDs, State Machines, and Microcontrollers. Since the transition region is steep and approximately linear, a properly-biased CMOS inverter digital logic gate may be used as a high-gain analog linear amplifier or even combined to form an opamp. The tolerance to noise can be measured by comparing the minimum input to the maximum output for each region of operation (on / off). The slope of this transition region is a measure of quality – steep (close to infinity) slopes yield precise switching. The VTC indicates that for low input voltage, the circuit outputs high voltage for high input, the output tapers off towards the low level. Ideally, the VTC appears as an inverted step function – this would indicate precise switching between on and off – but in real devices, a gradual transition region exists. From such a graph, device parameters including noise tolerance, gain, and operating logic levels can be obtained. Performance measurement Voltage transfer curve for a 20 μm inverter fabricated at North Carolina State Universityĭigital inverter quality is often measured using the voltage transfer curve (VTC), which is a plot of output vs. If no specific NOT gates are available, one can be made from the universal NAND or NOR gates, or an XOR gate by setting one input to high. Implementation determines the actual voltage, but common levels include (0, +5V) for TTL circuits.įurther information: NAND logic and NOR logic An inverter circuit serves as the basic logic gate to swap between those two voltage levels. Inverters can also be constructed with bipolar junction transistors (BJT) in either a resistor–transistor logic (RTL) or a transistor–transistor logic (TTL) configuration.ĭigital electronics circuits operate at fixed voltage levels corresponding to a logical 0 or 1 (see binary). Processing speed can also be improved due to the relatively low resistance compared to the NMOS-only or PMOS-only type devices. This configuration greatly reduces power consumption since one of the transistors is always off in both logic states. Alternatively, inverters can be constructed using two complementary transistors in a CMOS configuration. However, because current flows through the resistor in one of the two states, the resistive-drain configuration is disadvantaged for power consumption and processing speed. Since this "resistive-drain" approach uses only a single type of transistor, it can be fabricated at a low cost. Inverters can be constructed using a single NMOS transistor or a single PMOS transistor coupled with a resistor. If the applied input is low then the output becomes high and vice versa. Its main function is to invert the input signal applied. Electronic implementation Īn inverter circuit outputs a voltage representing the opposite logic-level to its input. A slash (/) before the variable is also used. Ī bar or overline ( ‾ ) above a variable can denote negation (or inversion or complement) performed by a NOT gate. Sometimes only the circle portion of the symbol is used, and it is attached to the input or output of another gate the symbols for NAND and NOR are formed in this way. To symbolize active-low input, sometimes the bubble is instead placed on the input line.
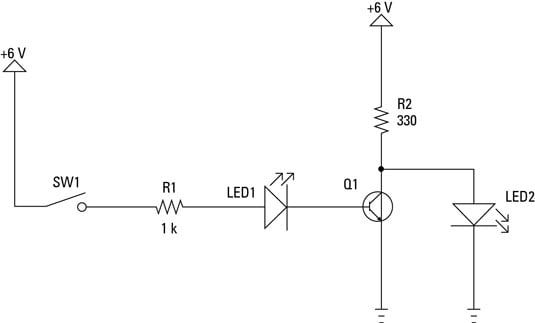
Input and output lines are attached to the symbol the bubble is typically attached to the output line. The traditional symbol for an inverter circuit is a triangle touching a small circle or "bubble". The terms "programmable inverter" or "controlled inverter" do not refer to this gate instead, these terms refer to the XOR gate because it can conditionally function like a NOT gate.
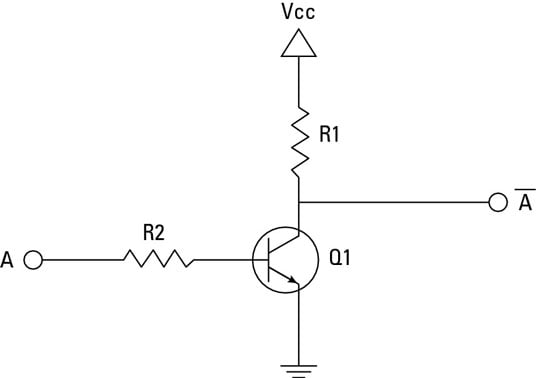
All other logic gates may be made from these three. Together with the AND gate and the OR gate, any function in binary mathematics may be implemented.

The NOT gate is one of three basic logic gates from which any Boolean circuit may be built up. It is also called the complement gate because it produces the ones' complement of a binary number, swapping 0s and 1s. Because it has only one input, it is a unary operation and has the simplest type of truth table. It is equivalent to the logical negation operator (¬) in mathematical logic. As with all binary logic gates, other pairs of symbols - such as true and false, or high and low - may be used in lieu of one and zero. Colloquially, this inversion of bits is called "flipping" bits. The NOT gate outputs a zero when given a one, and a one when given a zero. The bits are typically implemented as two differing voltage levels.ĭescription Inverter truth table It outputs a bit opposite of the bit that is put into it. In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. Logic gate implementing negation Traditional NOT gate (inverter) symbol


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
